当调用 BeanFactory.getBean 方法获取 Bean 时,如果 Bean 还未创建,则会触发 Bean 的创建,本文主要关注 Bean 的创建过程。
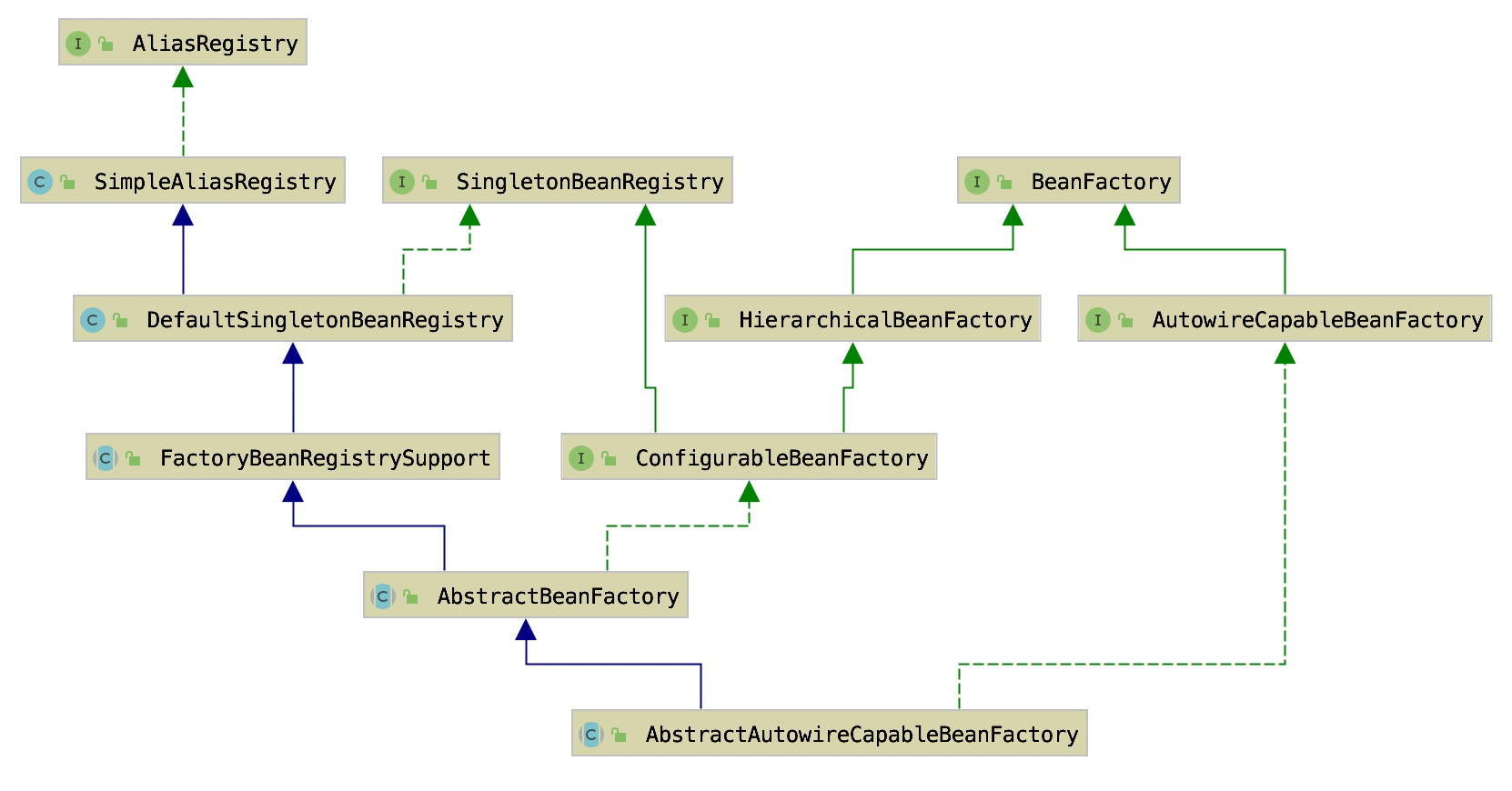
何时创建 在 Spring Bean 的获取过程 有提到 Singleton、Prototype 和 其他 Scope 类型的 Bean 创建,当获取不到所需的 Bean 实例时会触发创建 Bean,而这个创建 Bean 的操作是通过一个 createBean(beanName, mbd, args) 方法实现的。createBean(beanName, mbd, args) 是定义在 AbstractBeanFactory 中的一个方法,并且是在 AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory 中实现的,它的方法签名如下:
1 2 Object createBean (String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable Object[] args) throws BeanCreationException
AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory 是 AbstractBeanFactory 的子类,具有了 getBean 的能力。另外它还实现了 AutowireCapableBeanFactory 接口,需要提供 Autowire 的能力。
image-20200331011301319
AbstractBeanFactory 定义了 getBean 的流程,而把创建 Bean 的工作交给了子类去实现,AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory 是其子类,定义了 createBean 的流程。
当遇到以下几种情况时,都会触发 Bean 的创建
若 Bean 定义为 Singleton,并且从 DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry 的缓存中未获取到 Bean 若 Bean 定义为 Prototype,每一次获取 Bean 时 若 Bean 定义为其他 Scope,从 Scope 上下文中未获取到 Bean createBean 这是 AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory 最核心的一个方法,它的功能包括:创建 bean 实例、填充 bean 的属性、调用 postProcessor 等
解析 Bean Class 这里是为了确保 Bean Class 一定是解析过的
1 2 3 4 5 6 Class<?> resolvedClass = resolveBeanClass(mbd, beanName); if (resolvedClass != null && !mbd.hasBeanClass() && mbd.getBeanClassName() != null ) { mbdToUse = new RootBeanDefinition(mbd); mbdToUse.setBeanClass(resolvedClass); }
具体的实现如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 protected Class<?> resolveBeanClass(final RootBeanDefinition mbd, String beanName, final Class<?>... typesToMatch) throws CannotLoadBeanClassException { try { if (mbd.hasBeanClass()) { return mbd.getBeanClass(); } if (System.getSecurityManager() != null ) { return AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedExceptionAction<Class<?>>) () -> doResolveBeanClass(mbd, typesToMatch), getAccessControlContext()); } else { return doResolveBeanClass(mbd, typesToMatch); } } catch (PrivilegedActionException pae) { ClassNotFoundException ex = (ClassNotFoundException) pae.getException(); throw new CannotLoadBeanClassException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, mbd.getBeanClassName(), ex); } catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) { throw new CannotLoadBeanClassException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, mbd.getBeanClassName(), ex); } catch (LinkageError err) { throw new CannotLoadBeanClassException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, mbd.getBeanClassName(), err); } }
通常 BeanDefinition 中有设置 Class,上一步会直接返回。若未设置,则会调用 doResolveBeanClass 方法解析 Bean Class
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 private Class<?> doResolveBeanClass(RootBeanDefinition mbd, Class<?>... typesToMatch) throws ClassNotFoundException { ClassLoader beanClassLoader = getBeanClassLoader(); ClassLoader dynamicLoader = beanClassLoader; boolean freshResolve = false ; if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(typesToMatch)) { ClassLoader tempClassLoader = getTempClassLoader(); if (tempClassLoader != null ) { dynamicLoader = tempClassLoader; freshResolve = true ; if (tempClassLoader instanceof DecoratingClassLoader) { DecoratingClassLoader dcl = (DecoratingClassLoader) tempClassLoader; for (Class<?> typeToMatch : typesToMatch) { dcl.excludeClass(typeToMatch.getName()); } } } } String className = mbd.getBeanClassName(); if (className != null ) { Object evaluated = evaluateBeanDefinitionString(className, mbd); if (!className.equals(evaluated)) { if (evaluated instanceof Class) { return (Class<?>) evaluated; } else if (evaluated instanceof String) { className = (String) evaluated; freshResolve = true ; } else { throw new IllegalStateException("Invalid class name expression result: " + evaluated); } } if (freshResolve) { if (dynamicLoader != null ) { try { return dynamicLoader.loadClass(className); } catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) { if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace("Could not load class [" + className + "] from " + dynamicLoader + ": " + ex); } } } return ClassUtils.forName(className, dynamicLoader); } } return mbd.resolveBeanClass(beanClassLoader); }
准备方法 Overrides 1 mbdToUse.prepareMethodOverrides()
具体操作是交给了 AbstractBeanDefinition 的 prepareMethodOverrides 方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 public void prepareMethodOverrides () throws BeanDefinitionValidationException if (hasMethodOverrides()) { Set<MethodOverride> overrides = getMethodOverrides().getOverrides(); synchronized (overrides) { for (MethodOverride mo : overrides) { prepareMethodOverride(mo); } } } } protected void prepareMethodOverride (MethodOverride mo) throws BeanDefinitionValidationException int count = ClassUtils.getMethodCountForName(getBeanClass(), mo.getMethodName()); if (count == 0 ) { throw new BeanDefinitionValidationException( "Invalid method override: no method with name '" + mo.getMethodName() + "' on class [" + getBeanClassName() + "]" ); } else if (count == 1 ) { mo.setOverloaded(false ); } }
resolveBeforeInstantiation 给 BeanPostProcessors 一个机会,可以创建 bean 的代理出来,这样就不走后面的创建 bean 逻辑
1 2 3 4 Object bean = resolveBeforeInstantiation(beanName, mbdToUse); if (bean != null ) { return bean; }
当符合一定条件时:
通过 InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor 的 postProcessBeforeInstantiation 方法创建 Bean 实例 若上一步创建的实例不为空,则通过 BeanPostProcessor 的 postProcessAfterInitialization 方法对实例进行处理 整体的流程控制代码如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 protected Object resolveBeforeInstantiation (String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd) Object bean = null ; if (!Boolean.FALSE.equals(mbd.beforeInstantiationResolved)) { if (!mbd.isSynthetic() && hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors()) { Class<?> targetType = determineTargetType(beanName, mbd); if (targetType != null ) { bean = applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInstantiation(targetType, beanName); if (bean != null ) { bean = applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(bean, beanName); } } } mbd.beforeInstantiationResolved = (bean != null ); } return bean; }
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor 创建实例的代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 protected Object applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInstantiation (Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) { if (bp instanceof InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) { InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor ibp = (InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) bp; Object result = ibp.postProcessBeforeInstantiation(beanClass, beanName); if (result != null ) { return result; } } } return null ; }
创建好实例之后,BeanPostProcessor 的回调
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 public Object applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization (Object existingBean, String beanName) throws BeansException { Object result = existingBean; for (BeanPostProcessor processor : getBeanPostProcessors()) { Object current = processor.postProcessAfterInitialization(result, beanName); if (current == null ) { return result; } result = current; } return result; }
doCreateBean 若上一步未创建 Bean,则执行下面的 doCreateBean 创建 Bean 流程
1 Object beanInstance = doCreateBean(beanName, mbdToUse, args)
createBeanInstance 创建 java bean 并封装到 beanWrapper 中,执行完 beanWrapper 的初始化。
解析 Bean Class 判断 Bean Class 是否允许访问(public) 若设置了 instanceSupplier,则通过它创建 Bean 实例 若设置了 factoryMethodName,则通过工厂方法创建 若已经解析过构造函数,再次创建相同的 bean,则进行短路处理 通过 SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor 获取到构造函数,然后创建 Bean(区分有无参数) 使用默认的无参构造函数创建 Bean 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 protected BeanWrapper createBeanInstance (String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable Object[] args) Class<?> beanClass = resolveBeanClass(mbd, beanName); if (beanClass != null && !Modifier.isPublic(beanClass.getModifiers()) && !mbd.isNonPublicAccessAllowed()) { throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Bean class isn't public, and non-public access not allowed: " + beanClass.getName()); } Supplier<?> instanceSupplier = mbd.getInstanceSupplier(); if (instanceSupplier != null ) { return obtainFromSupplier(instanceSupplier, beanName); } if (mbd.getFactoryMethodName() != null ) { return instantiateUsingFactoryMethod(beanName, mbd, args); } boolean resolved = false ; boolean autowireNecessary = false ; if (args == null ) { synchronized (mbd.constructorArgumentLock) { if (mbd.resolvedConstructorOrFactoryMethod != null ) { resolved = true ; autowireNecessary = mbd.constructorArgumentsResolved; } } } if (resolved) { if (autowireNecessary) { return autowireConstructor(beanName, mbd, null , null ); } else { return instantiateBean(beanName, mbd); } } Constructor<?>[] ctors = determineConstructorsFromBeanPostProcessors(beanClass, beanName); if (ctors != null || mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == AUTOWIRE_CONSTRUCTOR || mbd.hasConstructorArgumentValues() || !ObjectUtils.isEmpty(args)) { return autowireConstructor(beanName, mbd, ctors, args); } ctors = mbd.getPreferredConstructors(); if (ctors != null ) { return autowireConstructor(beanName, mbd, ctors, null ); } return instantiateBean(beanName, mbd); }
applyMergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessors 调用 MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor 处理 beanDefinition。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 protected void applyMergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessors (RootBeanDefinition mbd, Class<?> beanType, String beanName) for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) { if (bp instanceof MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) { MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor bdp = (MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) bp; bdp.postProcessMergedBeanDefinition(mbd, beanType, beanName); } } }
这里可以对合并后的 BeanDefinition 进行处理,添加所需的东西,比如解析 Autowire 注解等
addSingletonFactory 如果是 Singleton bean,并且允许循环引用,并且当前 bean 正在创建中,则通过添加 SingletonFactory 的方式提前将 bean 暴露出去
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 boolean earlySingletonExposure = (mbd.isSingleton() && this .allowCircularReferences && isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)); if (earlySingletonExposure) { if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace("Eagerly caching bean '" + beanName + "' to allow for resolving potential circular references" ); } addSingletonFactory(beanName, () -> getEarlyBeanReference(beanName, mbd, bean)); }
暴露出去的 bean 还可以通过 SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor 的 getEarlyBeanReference 方法进一步处理
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 protected Object getEarlyBeanReference (String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, Object bean) Object exposedObject = bean; if (!mbd.isSynthetic() && hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors()) { for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) { if (bp instanceof SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) { SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor ibp = (SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) bp; exposedObject = ibp.getEarlyBeanReference(exposedObject, beanName); } } } return exposedObject; }
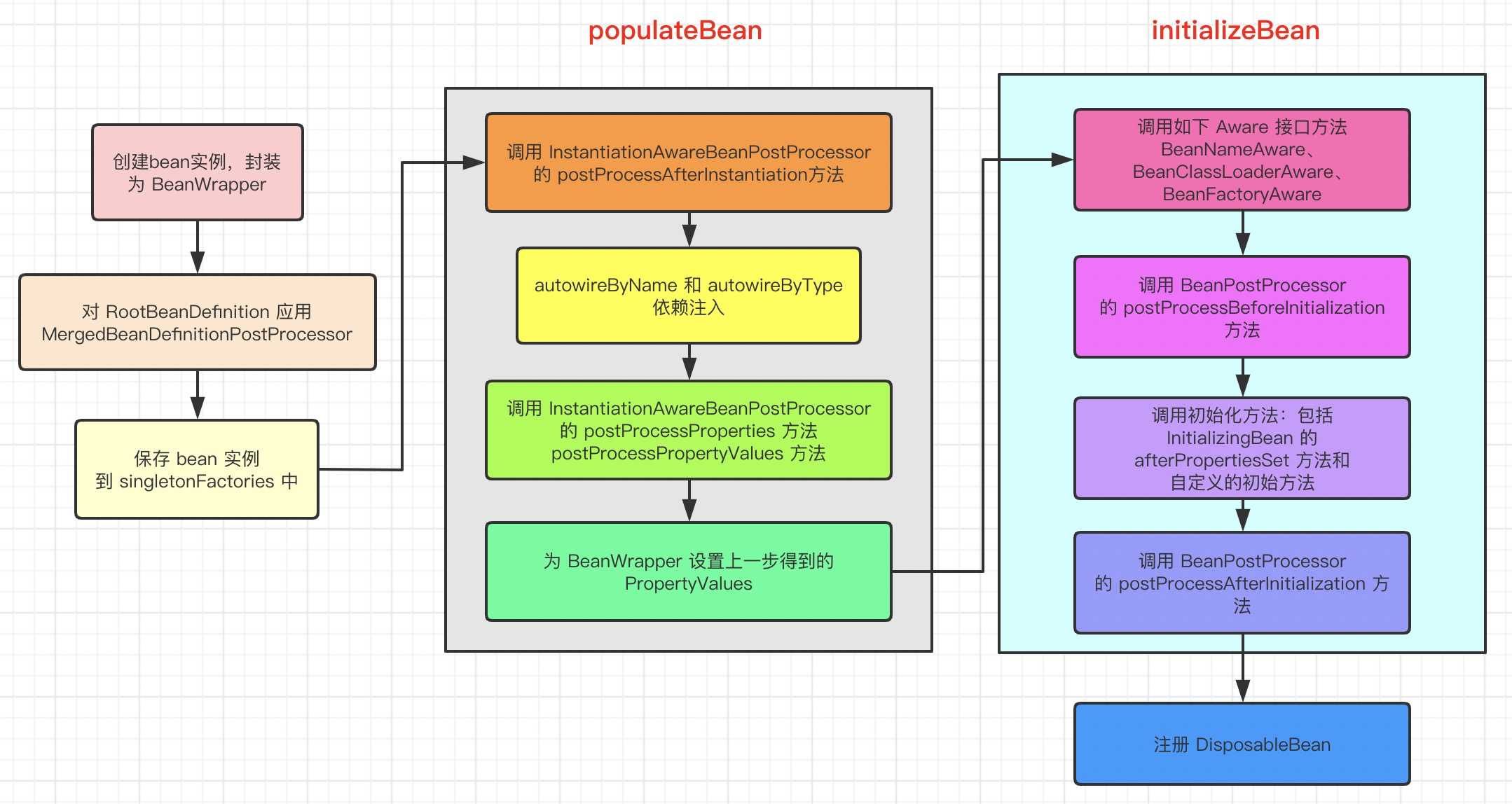
populateBean 下面就可以填充 bean 的属性,各种 autowire 都是在这里处理的
postProcessAfterInstantiation 这是在 properties 设置之前的操作,可以对 bean 的状态进行修改。若返回 false 则表示不需要后续的属性填充,直接返回
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 boolean continueWithPropertyPopulation = true ;if (!mbd.isSynthetic() && hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors()) { for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) { if (bp instanceof InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) { InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor ibp = (InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) bp; if (!ibp.postProcessAfterInstantiation(bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName)) { continueWithPropertyPopulation = false ; break ; } } } } if (!continueWithPropertyPopulation) { return ; }
其中 postProcessAfterInstantiation 的方法签名如下:
1 boolean postProcessAfterInstantiation (Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException
autowire byName 和 byType 对应 xml 中配置的 autowire="byType" 和 autowire="byName"
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 if (mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == AUTOWIRE_BY_NAME || mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE) { MutablePropertyValues newPvs = new MutablePropertyValues(pvs); if (mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == AUTOWIRE_BY_NAME) { autowireByName(beanName, mbd, bw, newPvs); } if (mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE) { autowireByType(beanName, mbd, bw, newPvs); } pvs = newPvs; }
postProcessProperties 如果存在 InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors,则回调 postProcessProperties 方法,Autowire 注解的依赖注入也是在这里处理的
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) { if (bp instanceof InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) { InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor ibp = (InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) bp; PropertyValues pvsToUse = ibp.postProcessProperties(pvs, bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName); if (pvsToUse == null ) { if (filteredPds == null ) { filteredPds = filterPropertyDescriptorsForDependencyCheck(bw, mbd.allowCaching); } pvsToUse = ibp.postProcessPropertyValues(pvs, filteredPds, bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName); if (pvsToUse == null ) { return ; } } pvs = pvsToUse; } }
postProcessProperties 方法的签名如下:
1 PropertyValues postProcessProperties (PropertyValues pvs, Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException
postProcessPropertyValues 方法的签名如下:
1 PropertyValues postProcessPropertyValues (PropertyValues pvs, PropertyDescriptor[] pds, Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException
applyPropertyValues 应用给定的 property values,解析指向其他 bean 的引用。必须使用深拷贝,这样才不会永久修改引用的属性值。
1 2 3 if (pvs != null ) { applyPropertyValues(beanName, mbd, bw, pvs); }
它的核心代码是:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 protected void applyPropertyValues (String beanName, BeanDefinition mbd, BeanWrapper bw, PropertyValues pvs) mpvs = (MutablePropertyValues) pvs; bw.setPropertyValues(mpvs); bw.setPropertyValues(new MutablePropertyValues(deepCopy)); }
initializeBean 初始化 bean,包括 aware、postProcessBeforeInitialization、InitializingBean 的 afterPropertiesSet、bean 自定义的 init 方法、postProcessAfterInitialization 等
invokeAwareMethods 调用 aware 方法,包括 BeanNameAware、BeanClassLoaderAware 和 BeanFactoryAware 对应的方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 private void invokeAwareMethods (final String beanName, final Object bean) if (bean instanceof Aware) { if (bean instanceof BeanNameAware) { ((BeanNameAware) bean).setBeanName(beanName); } if (bean instanceof BeanClassLoaderAware) { ClassLoader bcl = getBeanClassLoader(); if (bcl != null ) { ((BeanClassLoaderAware) bean).setBeanClassLoader(bcl); } } if (bean instanceof BeanFactoryAware) { ((BeanFactoryAware) bean).setBeanFactory(AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.this ); } } }
postProcessBeforeInitialization 调用 postProcessBeforeInitialization 方法
1 2 3 4 if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) { wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName); }
它会遍历调用所有的 BeanPostProcessor 的 postProcessBeforeInitialization 方法,如果有一个返回 null,则忽略后续的 BeanPostProcessor。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 public Object applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization (Object existingBean, String beanName) throws BeansException Object result = existingBean; for (BeanPostProcessor processor : getBeanPostProcessors()) { Object current = processor.postProcessBeforeInitialization(result, beanName); if (current == null ) { return result; } result = current; } return result; }
这是 bean 初始化之前的扩展点,可以对 bean 的初始化做一些准备工作,比如调用一些其他的 Aware 接口的 set 方法。例如 ApplicationContextAwareProcessor 的 postProcessBeforeInitialization 方法实现如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization (final Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException invokeAwareInterfaces(bean); return bean; } private void invokeAwareInterfaces (Object bean) if (bean instanceof Aware) { if (bean instanceof EnvironmentAware) { ((EnvironmentAware) bean).setEnvironment(this .applicationContext.getEnvironment()); } if (bean instanceof EmbeddedValueResolverAware) { ((EmbeddedValueResolverAware) bean).setEmbeddedValueResolver(this .embeddedValueResolver); } if (bean instanceof ResourceLoaderAware) { ((ResourceLoaderAware) bean).setResourceLoader(this .applicationContext); } if (bean instanceof ApplicationEventPublisherAware) { ((ApplicationEventPublisherAware) bean).setApplicationEventPublisher(this .applicationContext); } if (bean instanceof MessageSourceAware) { ((MessageSourceAware) bean).setMessageSource(this .applicationContext); } if (bean instanceof ApplicationContextAware) { ((ApplicationContextAware) bean).setApplicationContext(this .applicationContext); } } }
invokeInitMethods 调用初始化方法,包括 InitializingBean 的 afterPropertiesSet 方法,以及 bean 自定义的 init 方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 protected void invokeInitMethods (String beanName, final Object bean, @Nullable RootBeanDefinition mbd) throws Throwable { boolean isInitializingBean = (bean instanceof InitializingBean); if (isInitializingBean && (mbd == null || !mbd.isExternallyManagedInitMethod("afterPropertiesSet" ))) { ((InitializingBean) bean).afterPropertiesSet(); } if (mbd != null && bean.getClass() != NullBean.class) { String initMethodName = mbd.getInitMethodName(); if (StringUtils.hasLength(initMethodName) && !(isInitializingBean && "afterPropertiesSet" .equals(initMethodName)) && !mbd.isExternallyManagedInitMethod(initMethodName)) { invokeCustomInitMethod(beanName, bean, mbd); } } }
postProcessAfterInitialization 调用 postProcessAfterInitialization 方法
1 2 3 4 if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) { wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName); }
这里的控制逻辑与 postProcessBeforeInitialization 类似
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 public Object applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization (Object existingBean, String beanName) throws BeansException Object result = existingBean; for (BeanPostProcessor processor : getBeanPostProcessors()) { Object current = processor.postProcessAfterInitialization(result, beanName); if (current == null ) { return result; } result = current; } return result; }
这是 bean 初始化之后的扩展点,通常 postProcessAfterInitialization 方法不需要对 bean 做任何操作,直接原样返回
检查是否有冲突 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 if (earlySingletonExposure) { Object earlySingletonReference = getSingleton(beanName, false ); if (earlySingletonReference != null ) { if (exposedObject == bean) { exposedObject = earlySingletonReference; } else if (!this .allowRawInjectionDespiteWrapping && hasDependentBean(beanName)) { String[] dependentBeans = getDependentBeans(beanName); Set<String> actualDependentBeans = new LinkedHashSet<>(dependentBeans.length); for (String dependentBean : dependentBeans) { if (!removeSingletonIfCreatedForTypeCheckOnly(dependentBean)) { actualDependentBeans.add(dependentBean); } } if (!actualDependentBeans.isEmpty()) { throw new BeanCurrentlyInCreationException(beanName, "Bean with name '" + beanName + "' has been injected into other beans [" + StringUtils.collectionToCommaDelimitedString(actualDependentBeans) + "] in its raw version as part of a circular reference, but has eventually been " + "wrapped. This means that said other beans do not use the final version of the " + "bean. This is often the result of over-eager type matching - consider using " + "'getBeanNamesOfType' with the 'allowEagerInit' flag turned off, for example." ); } } } }
registerDisposableBeanIfNecessary 如果当前 bean 需要 destroy,则将其注册到 disposableBeans 中
Singleton 类型的 bean 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 if (mbd.isSingleton()) { registerDisposableBean(beanName, new DisposableBeanAdapter(bean, beanName, mbd, getBeanPostProcessors(), acc)); }
它实际上是调用了 DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry 的 registerDisposableBean 方法,将自己注册到了 disposableBeans 中
1 2 3 4 5 public void registerDisposableBean (String beanName, DisposableBean bean) synchronized (this .disposableBeans) { this .disposableBeans.put(beanName, bean); } }
其他类型的 bean 1 2 3 4 5 6 Scope scope = this .scopes.get(mbd.getScope()); if (scope == null ) { throw new IllegalStateException("No Scope registered for scope name '" + mbd.getScope() + "'" ); } scope.registerDestructionCallback(beanName, new DisposableBeanAdapter(bean, beanName, mbd, getBeanPostProcessors(), acc));
它是向 Scope 中注册了一个 DisposableBeanAdapter 类型的回调。DisposableBeanAdapter 封装了要 destroy 的 bean,在其 destroy 方法中进行相关操作
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 public void destroy () if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(this .beanPostProcessors)) { for (DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessor processor : this .beanPostProcessors) { processor.postProcessBeforeDestruction(this .bean, this .beanName); } } if (this .invokeDisposableBean) { try { ((DisposableBean) this .bean).destroy(); } catch (Throwable ex) { } } if (this .destroyMethod != null ) { invokeCustomDestroyMethod(this .destroyMethod); } else if (this .destroyMethodName != null ) { Method methodToCall = determineDestroyMethod(this .destroyMethodName); if (methodToCall != null ) { invokeCustomDestroyMethod(methodToCall); } } }
流程图 Spring Bean 创建的主要流程如下:
image-20200402015737100