XmlBeanFactory 是一个最简单的 BeanFactory 实现,它支持通过 xml 的形式配置和管理 bean。本文主要关注其解析 xml 和加载 BeanDefinition 的流程。
XmlBeanFactory 继承自 DefaultListableBeanFactory,后者是一个功能完备的 BeanFactory 实现类,XmlBeanFactory 在它的基础上增加了读取 xml 解析 BeanDefinition 的功能。XmlBeanFactory 并没有自己完成这些工作,而是交给了 XmlBeanDefinitionReader 类来实现。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 public class XmlBeanFactory extends DefaultListableBeanFactory private final XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(this ); public XmlBeanFactory (Resource resource, BeanFactory parentBeanFactory) throws BeansException super (parentBeanFactory); this .reader.loadBeanDefinitions(resource); } }
Document 的加载 在获取到表示资源的 Resource 对象之后,首先要从中读取 inputStream 并转换成用于表示 xml 文档的 Document 对象。
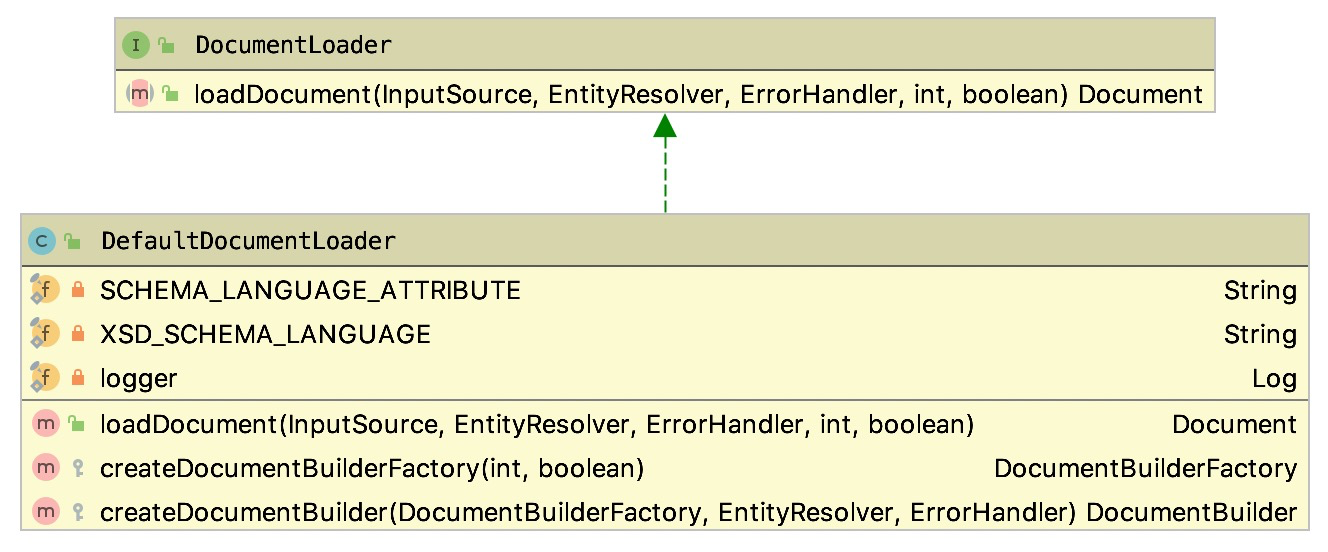
Document 的加载是委托给 DefaultDocumentLoader 类来处理的。DefaultDocumentLoader 是 DocumentLoader 的默认实现,它使用标准的 JAXP XML 解析器加载 Document。它的类继承结构如下图所示:
image-20200410011926136
loadDocument 方法用于解析输入流,生成 Document 对象,主要流程如下:
构建 DocumentBuilderFactory 通过 DocumentBuilderFactory 构建 DocumentBuilder 使用 builder 解析输入流,生成 Document 对象 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 public Document loadDocument (InputSource inputSource, EntityResolver entityResolver, ErrorHandler errorHandler, int validationMode, boolean namespaceAware) throws Exception DocumentBuilderFactory factory = createDocumentBuilderFactory(validationMode, namespaceAware); if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace("Using JAXP provider [" + factory.getClass().getName() + "]" ); } DocumentBuilder builder = createDocumentBuilder(factory, entityResolver, errorHandler); return builder.parse(inputSource); }
DocumentBuilderFactory 的构建 DocumentBuilderFactory 是通过它的工厂方法创建的,根据验证模式(DTD 模式、XSD 模式)的不同需设置不同的属性
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 protected DocumentBuilderFactory createDocumentBuilderFactory (int validationMode, boolean namespaceAware) throws ParserConfigurationException DocumentBuilderFactory factory = DocumentBuilderFactory.newInstance(); factory.setNamespaceAware(namespaceAware); if (validationMode != XmlValidationModeDetector.VALIDATION_NONE) { factory.setValidating(true ); if (validationMode == XmlValidationModeDetector.VALIDATION_XSD) { factory.setNamespaceAware(true ); try { factory.setAttribute(SCHEMA_LANGUAGE_ATTRIBUTE, XSD_SCHEMA_LANGUAGE); } catch (IllegalArgumentException ex) { throw pcex; } } } return factory; }
DocumentBuilder 的构建 DocumentBuilder 是通过 DocumentBuilderFactory 创建的,另外需要设置 EntityResolver 和 ErrorHandler
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 protected DocumentBuilder createDocumentBuilder (DocumentBuilderFactory factory, @Nullable EntityResolver entityResolver, @Nullable ErrorHandler errorHandler) throws ParserConfigurationException { DocumentBuilder docBuilder = factory.newDocumentBuilder(); if (entityResolver != null ) { docBuilder.setEntityResolver(entityResolver); } if (errorHandler != null ) { docBuilder.setErrorHandler(errorHandler); } return docBuilder; }
其中 EntityResolver 用于解析外部实体,需要根据 publicId 和 systemId 定位到资源,并将其解析为 InputResource 对象,如下是一个示例
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 public class MyResolver implements EntityResolver public InputSource resolveEntity (String publicId, String systemId) if (systemId.equals("http://www.myhost.com/today" )) { MyReader reader = new MyReader(); return new InputSource(reader); } else { return null ; } } }
Spring 通过 DelegatingEntityResolver 来完成 DTD 或 XSD 文档的解析。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 public InputSource resolveEntity (String publicId, @Nullable String systemId) throws SAXException, IOException if (systemId != null ) { if (systemId.endsWith(DTD_SUFFIX)) { return this .dtdResolver.resolveEntity(publicId, systemId); } else if (systemId.endsWith(XSD_SUFFIX)) { return this .schemaResolver.resolveEntity(publicId, systemId); } } return null ; }
DelegatingEntityResolver 并不是一个真正的执行者,它将 DTD 和 XSD 格式的文档的解析分别委托给 BeansDtdResolver 和 PluggableSchemaResolver
如下为 PluggableSchemaResolver 的解析方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 public InputSource resolveEntity (String publicId, @Nullable String systemId) throws IOException if (systemId != null ) { String resourceLocation = getSchemaMappings().get(systemId); if (resourceLocation != null ) { Resource resource = new ClassPathResource(resourceLocation, this .classLoader); try { InputSource source = new InputSource(resource.getInputStream()); source.setPublicId(publicId); source.setSystemId(systemId); return source; } catch (FileNotFoundException ex) { } } } return null ; }
它的 getSchemaMappings 方法会从 META-INF/spring.schemas 文件中读取配置信息(systemId 到 XSD 文档的映射关系),这样 resolveEntity 方法就可以根据 systemId 找到 class path 下的 XSD 文档并加载为 InputSource,从而避免了从网络下载文档的不稳定性
1 2 3 Properties mappings = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadAllProperties(this .schemaMappingsLocation, this .classLoader);
有了 DocumentBuilder 后就可以解析输入流了
1 return builder.parse(inputSource);
这里的 inputSource 是一个 InputSource 类型的实例,它封装了 inputStream,并且设置了编码。具体的 parse 流程就不贴出来了。
1 2 3 4 InputSource inputSource = new InputSource(inputStream); if (encodedResource.getEncoding() != null ) { inputSource.setEncoding(encodedResource.getEncoding()); }
创建 BeanDefinitionDocumentReader 上一步已经构建好了 Document 对象,接下来看下要怎么读取、解析和注册 BeanDefinition。
BeanDefinitionDocumentReader BeanDefinitionDocumentReader 用于读取 Document 对象,完成 BeanDefintion 的注册。
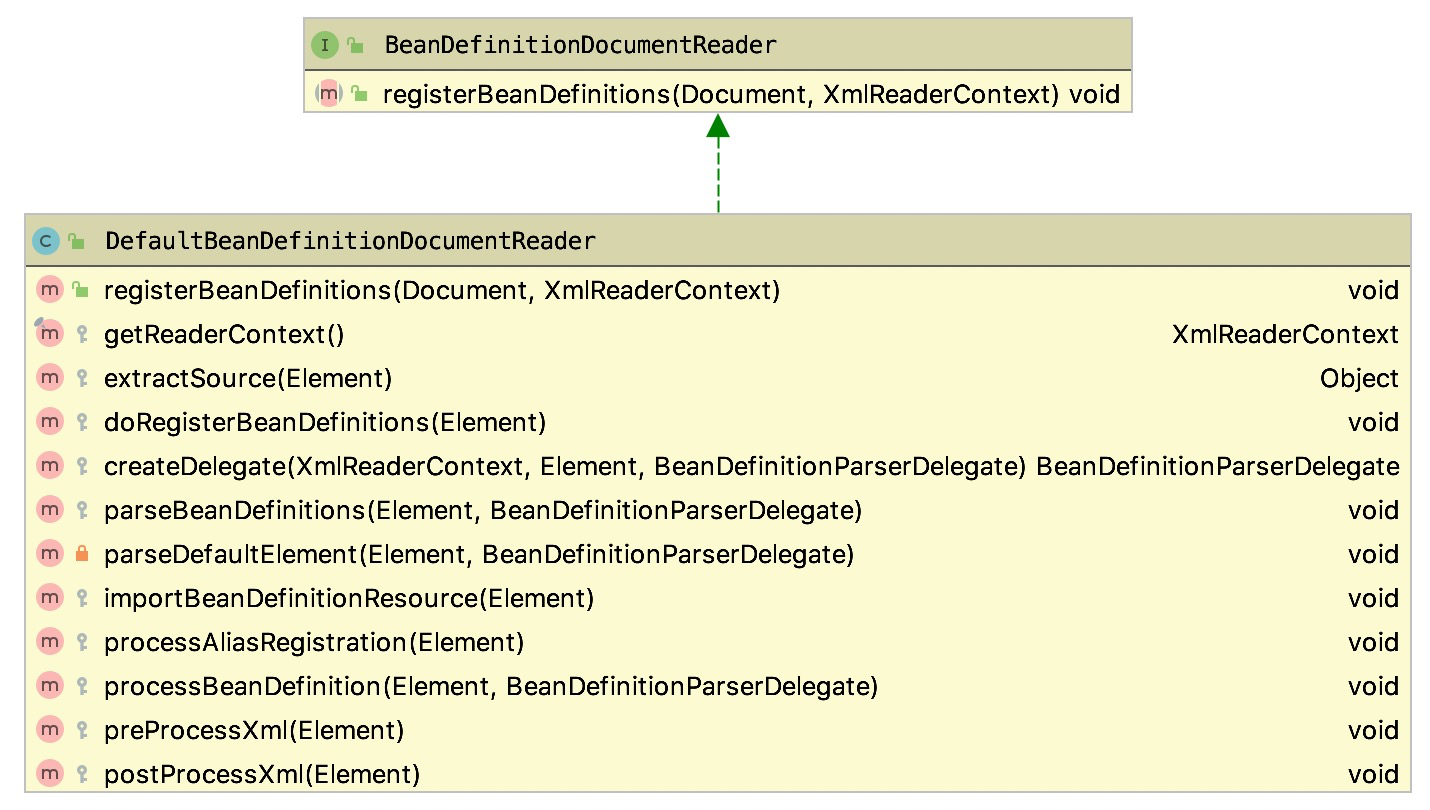
DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader 是 BeanDefinitionDocumentReader 的一个默认实现类,它的继承结构如下图所示:
image-20200410014832813
createBeanDefinitionDocumentReader 如下是创建 DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader 实例的代码,可以看出是通过反射创建的。
1 2 3 4 5 private Class<? extends BeanDefinitionDocumentReader> documentReaderClass = DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader.class; protected BeanDefinitionDocumentReader createBeanDefinitionDocumentReader () return BeanUtils.instantiateClass(this .documentReaderClass); }
registerBeanDefinitions 有了 BeanDefinitionDocumentReader 之后就可以处理 Document 了,这是通过它的 registerBeanDefinitions 方法实现的
1 2 void registerBeanDefinitions (Document doc, XmlReaderContext readerContext) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException ;
createReaderContext registerBeanDefinitions 入参中有一个 XmlReaderContext 对象,它是通过如下方式创建的:
1 2 3 4 public XmlReaderContext createReaderContext (Resource resource) return new XmlReaderContext(resource, this .problemReporter, this .eventListener, this .sourceExtractor, this , getNamespaceHandlerResolver()); }
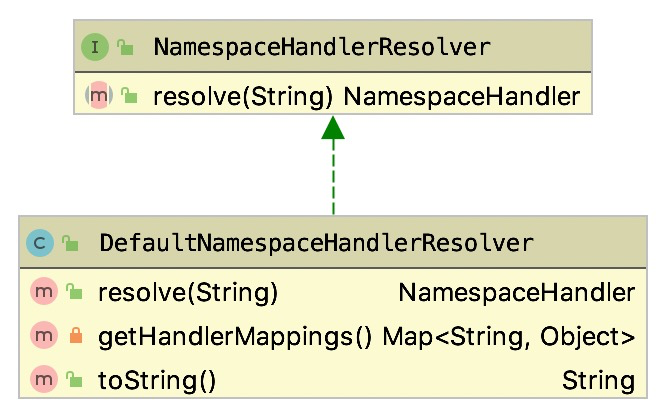
注意到最后一个参数是通过 getNamespaceHandlerResolver 方法获取到的,该方法返回了一个 NamespaceHandlerResolver 类型的对象,它的默认类是 DefaultNamespaceHandlerResolver
image-20200410015824553
NamespaceHandlerResolver 接口提供了一个 resolve 方法,它可以从 META-INF/spring.handlers 文件中读取 namespaceUri 到 NamespaceHandler 的映射关系,在使用时根据 namespaceUri 返回对应的 NamespaceHandler,这可以用于自定义 namespace 处理逻辑。如下是一个 META-INF/spring.handlers 文件的示例:
1 2 3 http\://www.springframework.org/schema/c=org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.SimpleConstructorNamespaceHandler http\://www.springframework.org/schema/p=org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.SimplePropertyNamespaceHandler http\://www.springframework.org/schema/util=org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.UtilNamespaceHandler
createDelegate 创建委托类,用于解析 XML bean 定义
1 2 3 BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate = new BeanDefinitionParserDelegate(readerContext); delegate.initDefaults(root, parentDelegate); return delegate;
initDefaults 方法会为 DocumentDefaultsDefinition 设置默认属性值,设置完之后发送事件通知
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 public void initDefaults (Element root, @Nullable BeanDefinitionParserDelegate parent) populateDefaults(this .defaults, (parent != null ? parent.defaults : null ), root); this .readerContext.fireDefaultsRegistered(this .defaults); }
填充默认值
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 protected void populateDefaults (DocumentDefaultsDefinition defaults, @Nullable DocumentDefaultsDefinition parentDefaults, Element root) String lazyInit = root.getAttribute(DEFAULT_LAZY_INIT_ATTRIBUTE); if (isDefaultValue(lazyInit)) { lazyInit = (parentDefaults != null ? parentDefaults.getLazyInit() : FALSE_VALUE); } defaults.setLazyInit(lazyInit); String merge = root.getAttribute(DEFAULT_MERGE_ATTRIBUTE); if (isDefaultValue(merge)) { merge = (parentDefaults != null ? parentDefaults.getMerge() : FALSE_VALUE); } defaults.setMerge(merge); String autowire = root.getAttribute(DEFAULT_AUTOWIRE_ATTRIBUTE); if (isDefaultValue(autowire)) { autowire = (parentDefaults != null ? parentDefaults.getAutowire() : AUTOWIRE_NO_VALUE); } defaults.setAutowire(autowire); if (root.hasAttribute(DEFAULT_AUTOWIRE_CANDIDATES_ATTRIBUTE)) { defaults.setAutowireCandidates(root.getAttribute(DEFAULT_AUTOWIRE_CANDIDATES_ATTRIBUTE)); } else if (parentDefaults != null ) { defaults.setAutowireCandidates(parentDefaults.getAutowireCandidates()); } if (root.hasAttribute(DEFAULT_INIT_METHOD_ATTRIBUTE)) { defaults.setInitMethod(root.getAttribute(DEFAULT_INIT_METHOD_ATTRIBUTE)); } else if (parentDefaults != null ) { defaults.setInitMethod(parentDefaults.getInitMethod()); } if (root.hasAttribute(DEFAULT_DESTROY_METHOD_ATTRIBUTE)) { defaults.setDestroyMethod(root.getAttribute(DEFAULT_DESTROY_METHOD_ATTRIBUTE)); } else if (parentDefaults != null ) { defaults.setDestroyMethod(parentDefaults.getDestroyMethod()); } defaults.setSource(this .readerContext.extractSource(root)); }
处理 profile 如果是默认的 namespace,则检查 profile 是否生效
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 if (this .delegate.isDefaultNamespace(root)) { String profileSpec = root.getAttribute(PROFILE_ATTRIBUTE); if (StringUtils.hasText(profileSpec)) { String[] specifiedProfiles = StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray( profileSpec, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate.MULTI_VALUE_ATTRIBUTE_DELIMITERS); if (!getReaderContext().getEnvironment().acceptsProfiles(specifiedProfiles)) { return ; } } }
parseBeanDefinitions 到这里要开始处理 Document 文档,解析 BeanDefinition 了。如果是默认的 namespace,则循环遍历节点。如果 Element 是默认 namespace 的,则需按照默认元素处理。其他情况按照自定义元素处理
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 protected void parseBeanDefinitions (Element root, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) if (delegate.isDefaultNamespace(root)) { NodeList nl = root.getChildNodes(); for (int i = 0 ; i < nl.getLength(); i++) { Node node = nl.item(i); if (node instanceof Element) { Element ele = (Element) node; if (delegate.isDefaultNamespace(ele)) { parseDefaultElement(ele, delegate); } else { delegate.parseCustomElement(ele); } } } } else { delegate.parseCustomElement(root); } }
默认 namspace 的处理 根据节点名的不同分别进行处理
解析 import 元素 解析 location,替换 placeholder,得到实际的 location
判断是否为绝对路径,如果是绝对路径,则直接通过 XmlBeanDefinitionReader 加载 BeanDefinition
1 int importCount = getReaderContext().getReader().loadBeanDefinitions(location, actualResources);
否则,按照相对路径处理
根据相对路径加载资源
1 Resource relativeResource = getReaderContext().getResource().createRelative(location)
判断 Resource 是否存在,若存在则可以直接加载
1 2 3 4 if (relativeResource.exists()) { importCount = getReaderContext().getReader().loadBeanDefinitions(relativeResource); actualResources.add(relativeResource); }
否则,通过 URL 拼接路径后加载
1 2 3 String baseLocation = getReaderContext().getResource().getURL().toString(); importCount = getReaderContext().getReader().loadBeanDefinitions( StringUtils.applyRelativePath(baseLocation, location), actualResources);
发送 import 完成事件
1 2 Resource[] actResArray = actualResources.toArray(new Resource[0 ]); getReaderContext().fireImportProcessed(location, actResArray, extractSource(ele));
解析 alias 元素 主要就是获取 alias name,然后往 AliasRegistry 中注册
1 getReaderContext().getRegistry().registerAlias(name, alias);
同样也会发送完成事件
1 getReaderContext().fireAliasRegistered(name, alias, extractSource(ele));
解析 bean 元素 这个是注册 BeanDefinition 的关键
委托 delegate 解析元素 1 BeanDefinitionHolder bdHolder = delegate.parseBeanDefinitionElement(ele);
主要就是解析 xml 元素的值,然后设置到 beanDefinition 中
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 AbstractBeanDefinition bd = createBeanDefinition(className, parent); parseBeanDefinitionAttributes(ele, beanName, containingBean, bd); bd.setDescription(DomUtils.getChildElementValueByTagName(ele, DESCRIPTION_ELEMENT)); parseMetaElements(ele, bd); parseLookupOverrideSubElements(ele, bd.getMethodOverrides()); parseReplacedMethodSubElements(ele, bd.getMethodOverrides()); parseConstructorArgElements(ele, bd); parsePropertyElements(ele, bd); parseQualifierElements(ele, bd); bd.setResource(this .readerContext.getResource()); bd.setSource(extractSource(ele)); return bd;
如果 xml 中未设置 bean 的 id 和 name,还要生成一个唯一的 id
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 if (containingBean != null ) { beanName = BeanDefinitionReaderUtils.generateBeanName( beanDefinition, this .readerContext.getRegistry(), true ); } else { beanName = this .readerContext.generateBeanName(beanDefinition); String beanClassName = beanDefinition.getBeanClassName(); if (beanClassName != null && beanName.startsWith(beanClassName) && beanName.length() > beanClassName.length() && !this .readerContext.getRegistry().isBeanNameInUse(beanClassName)) { aliases.add(beanClassName); } }
最终的结果会封装为 BeanDefinitionHolder
1 2 return new BeanDefinitionHolder(beanDefinition, beanName, aliasesArray);
进行必要的装饰 1 bdHolder = delegate.decorateBeanDefinitionIfRequired(ele, bdHolder);
前面提到了 NamespaceHandler 的注册,这里就是用它进行 decorate 的
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 if (namespaceUri != null && !isDefaultNamespace(namespaceUri)) { NamespaceHandler handler = this .readerContext.getNamespaceHandlerResolver().resolve(namespaceUri); if (handler != null ) { BeanDefinitionHolder decorated = handler.decorate(node, originalDef, new ParserContext(this .readerContext, this , containingBd)); if (decorated != null ) { return decorated; } } else if (namespaceUri.startsWith("http://www.springframework.org/" )) { error("Unable to locate Spring NamespaceHandler for XML schema namespace [" + namespaceUri + "]" , node); } else { } }
注册最终装饰过的实例 1 BeanDefinitionReaderUtils.registerBeanDefinition(bdHolder, getReaderContext().getRegistry());
如下是 BeanDefintion 注册的相关代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 public static void registerBeanDefinition ( BeanDefinitionHolder definitionHolder, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException { String beanName = definitionHolder.getBeanName(); registry.registerBeanDefinition(beanName, definitionHolder.getBeanDefinition()); String[] aliases = definitionHolder.getAliases(); if (aliases != null ) { for (String alias : aliases) { registry.registerAlias(beanName, alias); } } }
主要是往 BeanDefinitionRegistry 中注册 beanName 到 BeanDefintion 的映射关系,如果有别名,还需要一并注册进去
发送注册通知事件 1 getReaderContext().fireComponentRegistered(new BeanComponentDefinition(bdHolder))
解析嵌套 bean 元素 递归处理元素
1 doRegisterBeanDefinitions(ele);
自定义 namspace 的处理 Spring 还可以自定义 XSD 元素,并提供对应的元素处理器
getNamespaceURI 获取 element 的 namespace uri
1 2 3 public String getNamespaceURI (Node node) return node.getNamespaceURI(); }
getNamespaceHandler 1 NamespaceHandler handler = this .readerContext.getNamespaceHandlerResolver().resolve(namespaceUri);
首先要获取 NamespaceHandlerResolver,取到的是 DefaultNamespaceHandlerResolver,这是在前面 createReaderContext 的时候创建的 根据 namespaceUri 获取 NamespaceHandler 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 public NamespaceHandler resolve (String namespaceUri) Map<String, Object> handlerMappings = getHandlerMappings(); Object handlerOrClassName = handlerMappings.get(namespaceUri); if (handlerOrClassName == null ) { return null ; } else if (handlerOrClassName instanceof NamespaceHandler) { return (NamespaceHandler) handlerOrClassName; } else { String className = (String) handlerOrClassName; try { Class<?> handlerClass = ClassUtils.forName(className, this .classLoader); if (!NamespaceHandler.class.isAssignableFrom(handlerClass)) { throw new FatalBeanException("Class [" + className + "] for namespace [" + namespaceUri + "] does not implement the [" + NamespaceHandler.class.getName() + "] interface" ); } NamespaceHandler namespaceHandler = (NamespaceHandler) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(handlerClass); namespaceHandler.init(); handlerMappings.put(namespaceUri, namespaceHandler); return namespaceHandler; } catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) { throw new FatalBeanException("Could not find NamespaceHandler class [" + className + "] for namespace [" + namespaceUri + "]" , ex); } catch (LinkageError err) { throw new FatalBeanException("Unresolvable class definition for NamespaceHandler class [" + className + "] for namespace [" + namespaceUri + "]" , err); } } }
其中 HandlerMapping 是解析 META-INF/spring.handlers 的结果
使用 NamespaceHandler 解析元素 1 2 return handler.parse(ele, new ParserContext(this .readerContext, this , containingBd));
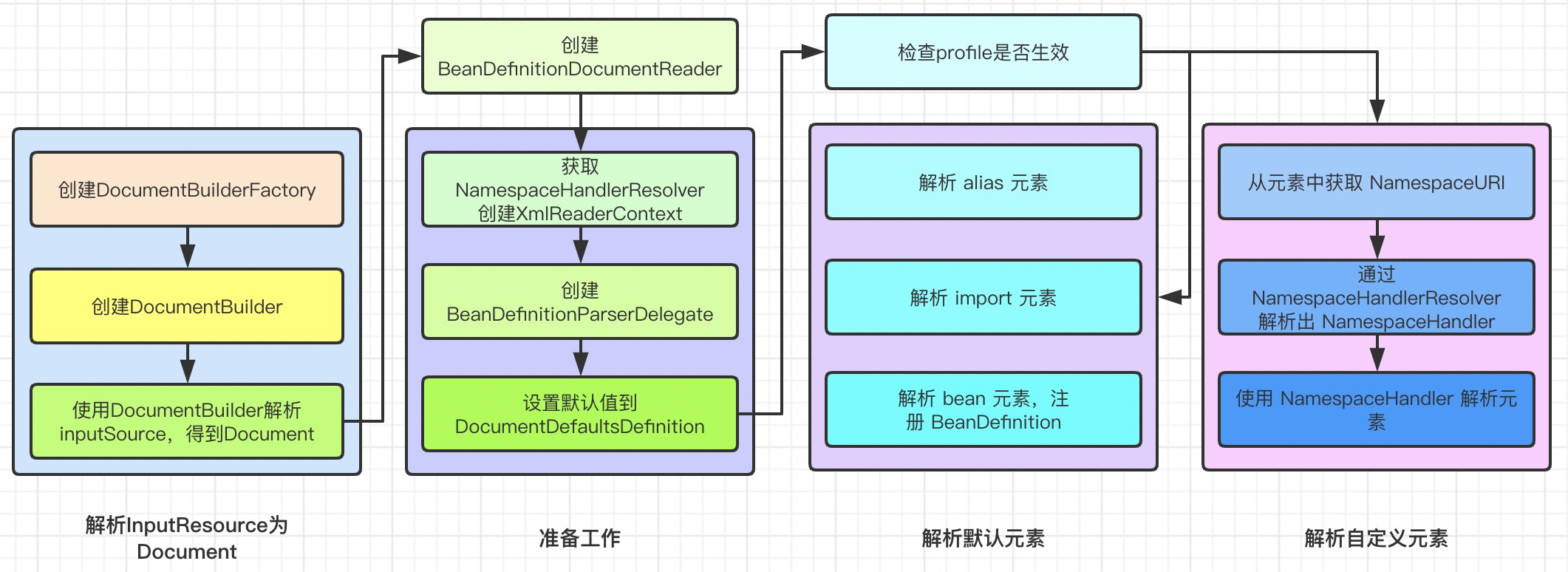
整体流程 下图是整体处理流程
image-20200411125807780
预览: